Our Solutions: Consulting
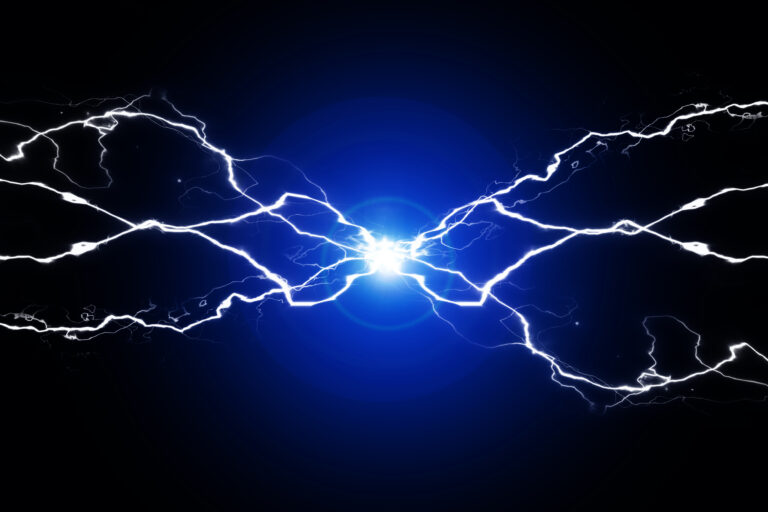

An electrostatic ignition source is a discharge (commonly referred to as a spark) resulting from the accumulation and discharge of electrostatic charges. Electrostatic charge generation most frequently occurs when any two materials – liquids and/or solids – make contact with each other and then separate.
The generation and accumulation of electrostatic charge is not generally in and of itself hazardous. Rather, a hazard is created when the static accumulation gives rise to electrostatic discharges that are sufficiently energetic to ignite a surrounding combustible dust, flammable liquid, or gas atmosphere.
For an electrostatic hazard to occur, the following criteria must be fulfilled:
To prevent the accumulation of hazardous levels of electrostatic charge and consequently energetic sparks, the electrical resistance to the ground of all conductive items of a plant including metal pipes, equipment, vessels, and containers should be checked. If the resistance is greater than 10 ohms, a direct ground connection will be required. Additionally, it is important that the ground connections are checked regularly and that their purpose is known to the operators and maintenance personnel.
With decades of experience in managing combustible dust hazards, flammable solvents, and gases, our engineers will partner with you to identify, assess, and control electrostatic hazards in your new or existing facility.
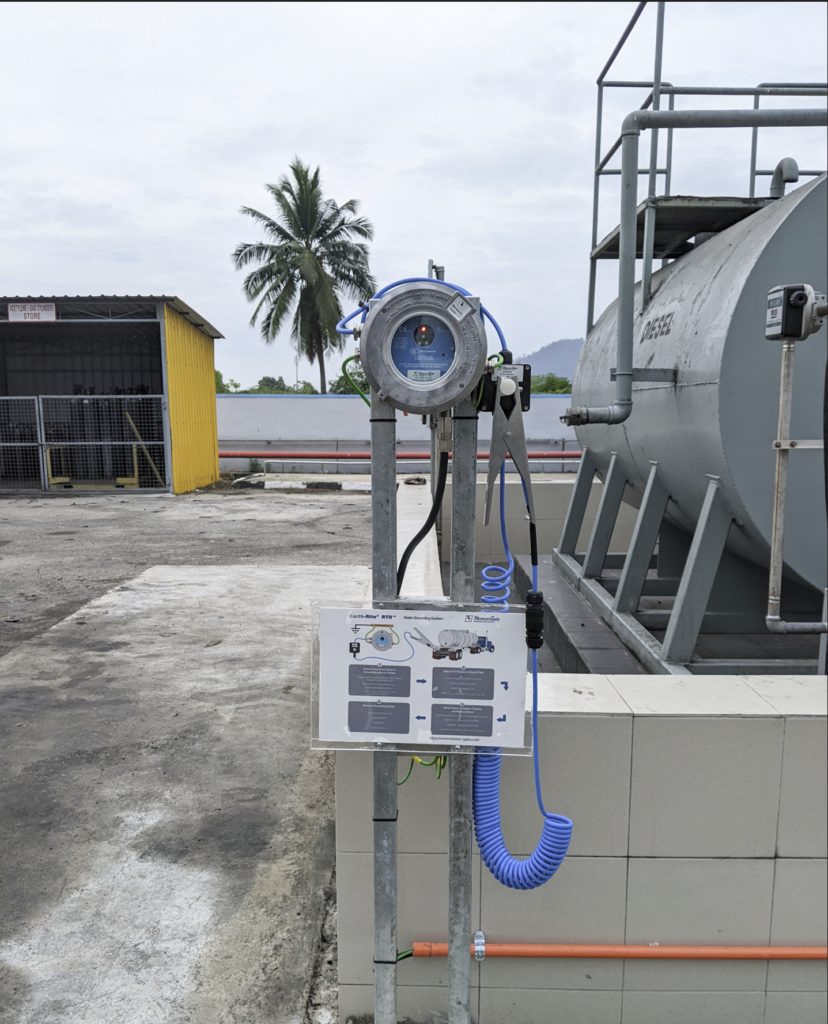
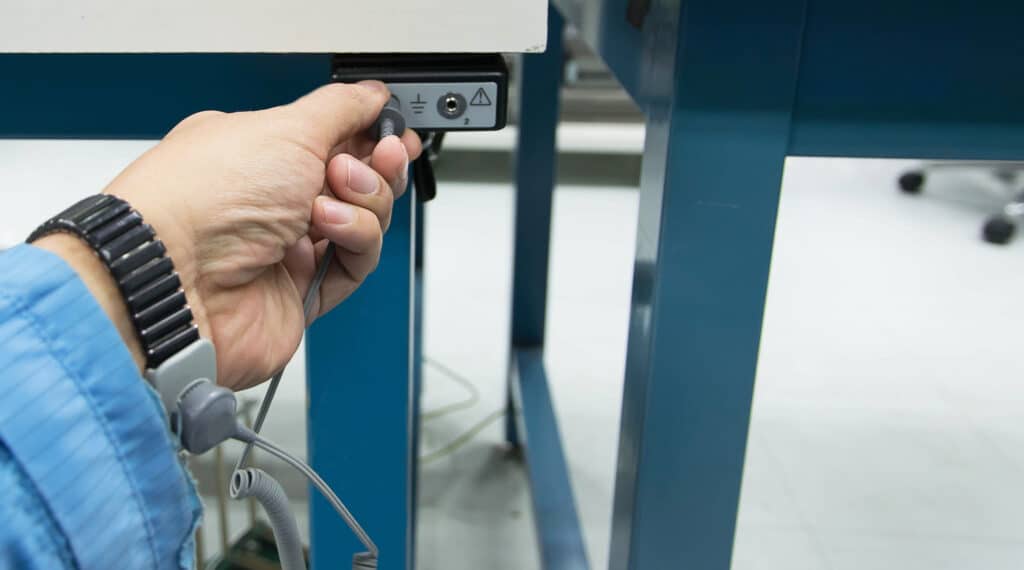


Sigma-HSE has the required resources, knowledge, and experience to conduct a comprehensive Electrostatic Hazards Assessment and recommend safe, pragmatic, and cost-effective solutions for controlling electrostatic hazards.
At Sigma-HSE, we can assist you in identifying the areas in a facility where flammable atmospheres and combustible dust can be found in both new and existing facilities and guide you through the complexities of controlling electrostatic hazards.
Electrostatic hazard analysis focuses on hazards that can be caused by static charge generation, build-up, and discharges that could serve as ignition sources to cause fire or explosion hazards. Sigma-HSE’s Electrostatic Hazard Assessment/Analysis will:
Ignition hazards from static electricity can be controlled by the following methods:
The human body is an electrical conductor and can accumulate a static charge if insulated from the ground. This charge can be generated by contact and separation of footwear with floor coverings, by induction, or by participation in various manufacturing operations. Where ignitable mixtures exist, the potential for ignition from the charged human body exists and means to prevent accumulation of static electric charge on the human body might be necessary. Steps to prevent charge accumulation include the use of the following:
Static electricity is a natural by-product of common industrial processes. In these settings, friction, contact and separation, and rapid heat changes can cause static buildup and discharge. Some common causes of static electricity in industrial settings include:
NFPA77 provides guidance on “identifying, evaluating, and controlling static electric hazards for the purpose of preventing fires and explosions. Other applicable codes and standard includes API RP 2003: Protection Against Ignitions Arising Out of Static, Lightning, and Stray Currents and IEC 60079-32-1: Electrostatic hazards – guidance.
Some dangers posed by static electricity are:
Electrostatic hazard assessments are typically performed by a team of engineers, including a process engineer and an electrical engineer. The team may also include client personnel and others knowledgeable of the process and operating procedures. Specialists from plant operations and health, safety, and environment (HSE) may also be involved.
Our expert consultants undertake an Electrostatic Hazard Assessment in a holistic way to eliminate potential fire and explosion hazards and risks that could affect plant personnel.
Sigma-HSE can assist you in identifying the areas in new and existing facilities where flammable atmospheres and combustible dust can be found and guide you through the complexities of the Electrostatic Hazard Assessment.
By implementing best practices, our actionable insights determine what practicable control measures and recommendations should be made for your company to optimize safety and reduce the level of risk to people, business, and the environment.
If you find yourself asking, ‘Do I need an Electrostatic Hazard Assessment?’, connect with us today. Our Electrostatic Hazard Assessment experts can answer any preliminary questions you may have.
Protect business, people, workplace and the environment from potentially unsafe equipment in hazardous zones and comply with explosive atmospheres regulations. Learn more about how we can assist you today.

Are you visiting Sigma-HSE from outside your region? Visit your regional site for more relevant process safety solutions.